Innovative Coating Technologies
- environmentally friendly
- saving resources
- efficient
- productive
- clean
PVT Plasma und Vakuum Technik GmbH has its focus on the development of ion and plasma-assisted vacuum coating technologies, particularly on following processes:
- PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition), by
Arc-Evaporation and
Magnetron-Sputtering - PECVD (Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Depositen)
However, should customer applications require, also combinations of different processes might be used, such as
- Electroplating + PVD
- Electrostatic powder coating + PVD
- Arc evaporation + Magnetron sputtering
- Plasma-nitriding + PVD
The application of such process combinations will only be applied as long as the advantages for the customers prevail concerning the lifetime and the longevity of the coated parts, taking into account the total cost.
PVD
(Physical Vapor Deposition)
PVT is considered as one of the early pioneers of hard coatings by PVD-processes, in particular using the arc evaporation with large area evaporators.
The complete PVD-process starts with putting the pre-cleaned (by aqueous solution) parts into the pre-heated vacuum chamber. Thereafter a fully automatic process runs through the following steps:
- Pre-heating of the substrate to the required coating temperature
- Sputter-etching, aka ion-etching or sputtercleaning
- Metall-ion-etching
- Deposition
- Cool down
After venting the vacuum chamber the coated parts are moved out of the chamber. For the deposition the coating material is transferred into the vapor phase either by magnetron sputtering or by arc evaporation or directly as a gas bleeding into the vacuum chamber.
PVD describes a variety of vacuum deposition methods to deposit thin films and coatings. These methods are characterized by processes in which material is transferred from the solid phase into the vapor phase and then back to thin solid films.
| PDA (Plasma Diffused Arc) | |||||
| HiParc (High Power Pulsed Arc) | |||||
| Hybrid PP | |||||
| Pulse Plasma Nitriding + Arc-evaporation | |||||
| Magnetron Sputtering | |||||
| HiPIMS (High Power Impuls Magnetron Sputtering) | |||||
| HiPIMS V+ | |||||
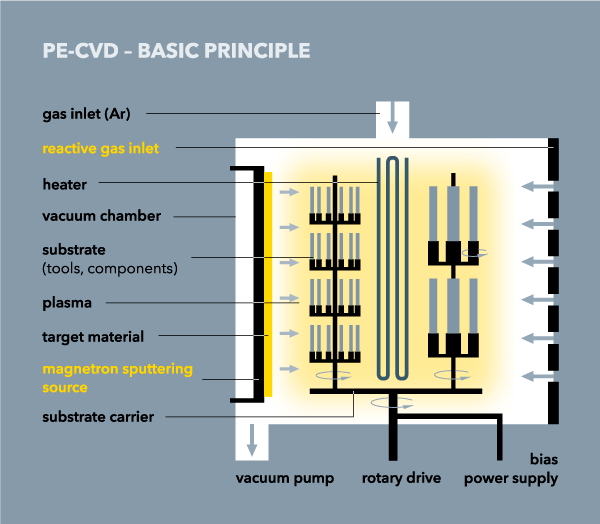
PECVD
(Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition)
Arc evaporation or magnetron sputtering are used to transfer the coating material from the solid phase into the vapor phase for deposition. PECVD is a third method where gases are fed into the vacuum chamber from which the coatings are synthesized.
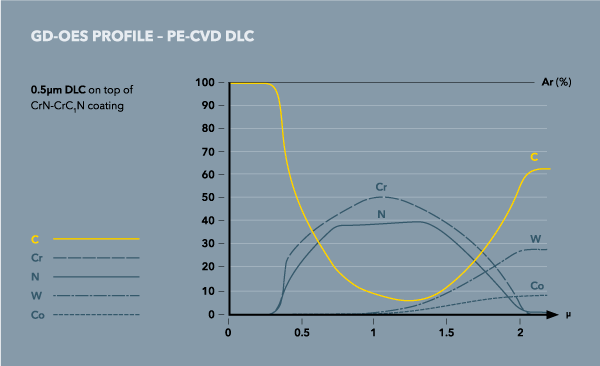
When using a PECVD-process, as with CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition), only gases are used. For PECVD the deposition temperatures are considerably lower (100–600 °C) compared to the classical CVD with temperatures in the rage of 1000 °C and higher. The plasma is used to enforce the reaction as well as the dissociation of the reactive gases, such as C₂H₂ or CH₄ during the deposition of DLC (Diamond Like Carbon) coatings.
Also combinations of processes such as
- PECVD + magnetron sputtering
- PECVD + arc evaporation
are used.
To deposit well adherent DLC-coatings adhesive layers have to be deposited prior forming DLC. Cr (Chromium), deposited by arc evaporation, is an excellent candidate to improve the adhesion of DLC.